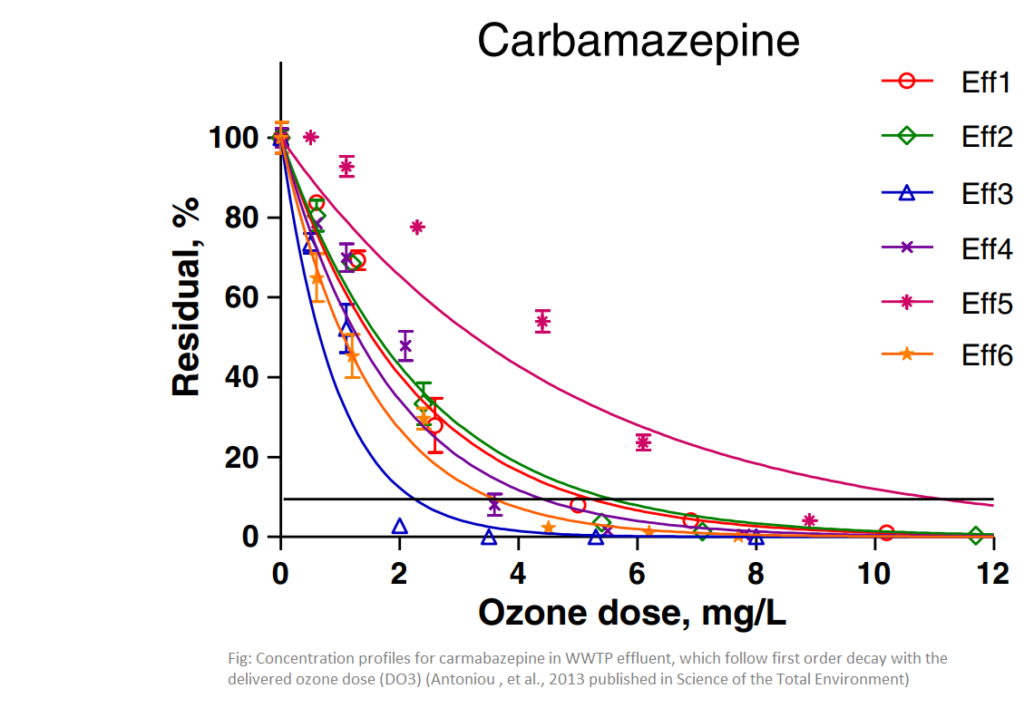
Required ozone dosage
The aim of this study was to investigate the ozone dosage required to remove active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) from biologically treated wastewater of varying quality, originated from different raw wastewater and wastewater treatment processes when treated with different O3 doses (0.5-12.0 mg/L ozone) in bench-scale experiments.
Ozone dose requirements were found to vary significantly between effluents depending on their matrix characteristics. The specific ozone dose was then normalized to the dissolved organic carbon (DOC) of each effluent. The DDO3/DOC ratios were comparable for each API between the effluents. 15 of the 42 investigated APIs could be classified as easily degradable (DDO3/DOC≤0.7), while 19 were moderately degradable (0.73-treatment (DDO3/DOC >1.4) Furthermore, we predict that a reasonable estimate of the ozone dose required to remove any of the investigated APIs may be attained by multiplying the experimental average DDO3/DOC obtained with the actual DOC of any effluent.
Paper: Required ozone doses for removing pharmaceuticals from wastewater effluents.
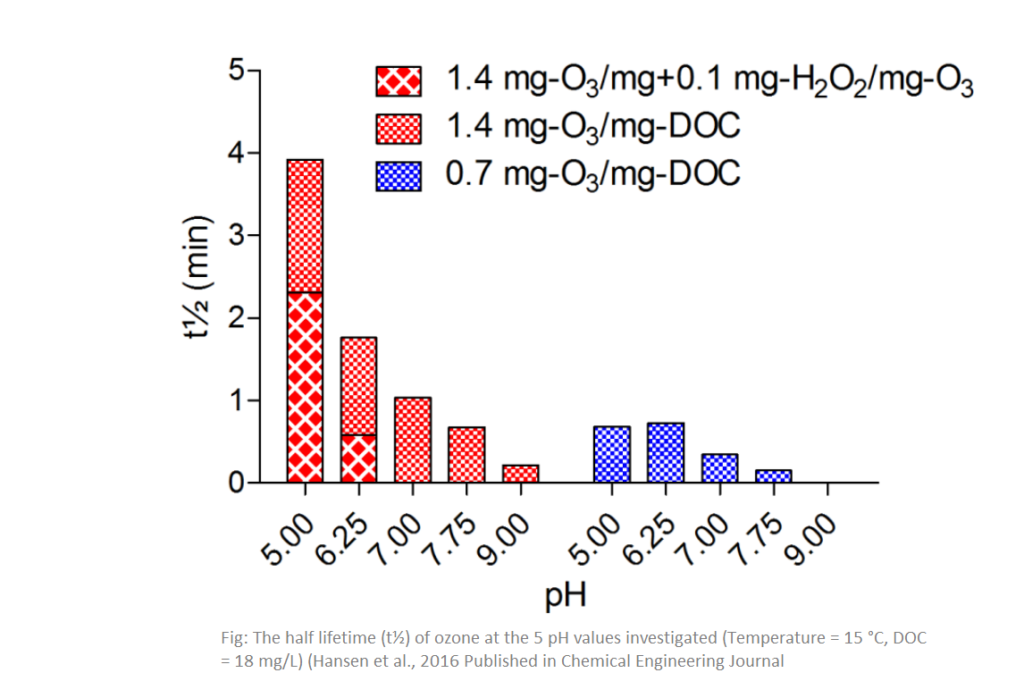
Ozone life time
Ozonation aimed at removing pharmaceuticals was studied in an effluent from an experimental pilot system using staged Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) tanks for the optimal biological treatment of wastewater from a medical care unit of Aarhus University Hospital. Dissolved Organic Carbon (DOC) and pH in samples varied considerably, and the effect of these two parameters on ozone lifetime and the efficiency of ozone in removing pharmaceuticals were determined. The pH in the effluent varied from 5.0 to 9.0 resulting in approximately a doubling of the required ozone dose at the highest pH for each pharmaceutical. DOC varied from 6 to 20 mg-DOC/L. The ozone required for removing each pharmaceutical, varied linearly with DOC and thus, ozone doses normalized to DOC (specific ozone dosis) agreed between water samples (typically within 15%). At neutral pH the specific ozone dose required to remove the easiest degradable pharmaceutical, sulfadiazine, was 0.50±0.04 mg-O3/mg-DOC and the most recalcitrant, diatrizoic acid, required 4.7±0.6 mg-03/mg-DOC. The lifetime of ozone increased drastically in the higher end of the indicated dosage. At the lowest observed pH of 5.0, its lifetime was quadrupled to 20 min which influences the design of the reaction tank. The addition of 0.1 mg-H202 per 1 mg-O3 mitigated the prolonged lifetime without a corresponding influence in the pharmaceutical removal efficiency of ozone.
Paper: Ozonation for source treatment of pharmaceuticals in hospital wastewater.